Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is a cancer that starts in the liver, hence also called as primary liver cancer. Cancer that arise in other organs and spread to liver are called as secondary liver cancer or metastatic tumor. HCC is commonly associated with any type of existing liver cirrhosis.

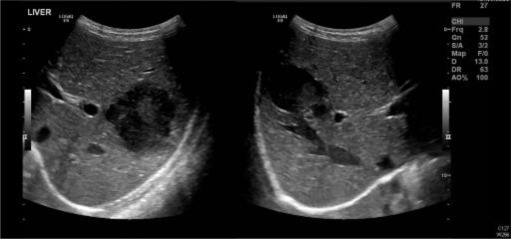
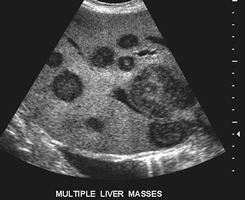
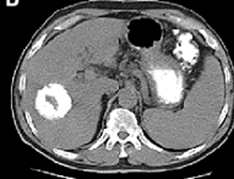
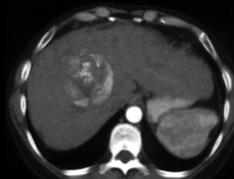
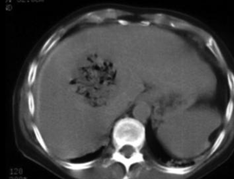
Interventional radiologists are uniquely skilled in using the vascular system to deliver targeted treatments via tubes and catheters throughout the body. In treating cancer patients, interventional radiologists can attack the cancer tumor from inside the body by using embolization and/ or radiofrequency heat. without medicating or affecting other parts of the body.
Tumors need a blood supply, which they themselves generate, to feed themselves and grow.
In treating cancer patients, interventional radiologists use either particle embolization to cut off the blood supply to the tumor , or deliver radiation particles to a tumor (radioembolization), or combine this technique with chemotherapy to deliver the cancer drug directly to the tumor (chemoembolization) or administer heat to kill the cancer cells by radiofrequency ablation or Microwave ablation or freeze the tumor by cyroablation.

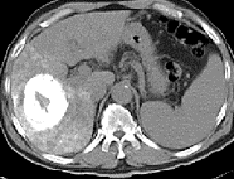
Chemoembolization is a minimally invasive treatment for liver cancer that can be used in case of large tumours, or when the tumor is in a location that cannot be treated with RFA, or in combination with RFA or other treatments.


Percutaneous radio frequency ablation (RFA) is an exciting approach to destroying inoperable primary or metastatic tumors in the liver. RFA serves as a bridge for transplant candidates, especially in relation to small primary lesions.
Percutaneous RFA is a minimally invasive, repeatable procedure , performed under radiological guidance.. RFA results in a higher rate of complete necrosis and requires fewer treatment sessions. Long-term survival rates are also better with RFA. RFA in combination with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is also an effective treatment for inoperable hepatic tumors.
In RFA, a needle is inserted into the liver, usually under the guidance of ultrasonography or CT. Once placed within the tumor, a generator is used to deliver radiofrequency energy. Heat is generated at the site of the lesion through frictional heat produced by rapid agitation of adjacent cells and produces destruction of the tumor. . Above 60ºC, cell death occurs almost instantly. Approximately 15-30 minutes are required to perform a 3-5 cm ablation.
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) can be performed with local anesthesia and mild sedation. The patient is often able to go home the same or next day. This technology is used widely in Europe, Japan and the United States.


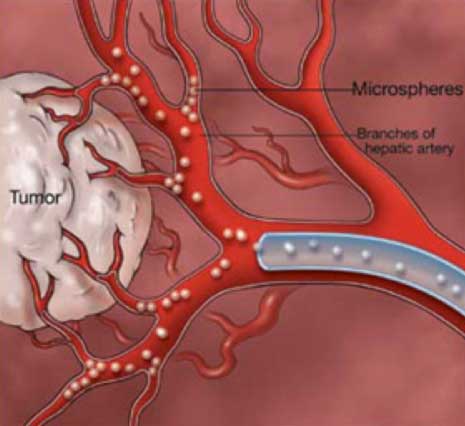
Radioembolization is very similar to chemoembolization but with the use of radioactive microspheres. This therapy is used to treat both primary and metastatic liver tumors.
This treatment incorporates the radioactive isotope Yttrium-90 into the embolic spheres to deliver radiation directly to the tumor. These beads are injected through a catheter from the groin into the liver artery supplying the tumor. The beads become lodged within the tumor vessels where they exert their local radiation that causes cell death. This technique allows for a higher, local dose of radiation to be used, without subjecting healthy tissue in the body to the radiation. The Yttrium-90 radiates from within and, since it is administered in the hepatic artery, it can be viewed as "internal" radiation.
Radioembolization is a palliative, not a curative, treatment- patients benefit by extending their lives and improving their quality of life. It is a relatively new therapy that has been effective in treating primary and metastatic liver cancers. It is performed as an outpatient treatment. There are fewer side effects from this treatment compared to standard cancer treatments, with the main one being fatigue for five to seven days.

Cryoablation is similar to RFA in that the energy is delivered directly into the tumor by a probe that is inserted through the skin. But rather than killing the tumor with heat, cryoablation uses an extremely cold gas to freeze it. This technique has been used for many years by surgeons in the operating room, but in the last few years, the needles have become small enough to be used by interventional radiologists through a small nick in the skin, without the need for an operation. The "ice ball" that is created around the needle grows in size and destroys the frozen tumor cells.
Interventional radiology is playing a role in developing new techniques that may improve cancer treatment in the future, including the use of magnetic particles to draw cancer-killing agents into tumors; and the delivery of genetic material, called gene therapy, to fight or prevent cancers. These techniques are still investigational, but they offer new hope in the war against cancer.
"Magnetic"Chemotherapy
Interventional radiologists are currently investigating a new technique in which magnets are used to pull chemotherapy drugs into tumors. Microscopic magnetic particles are attached to the cancer-killing drugs and infused through a catheter into the blood vessel that feeds the tumor. A rare earth magnet is positioned over the patient’s body directly above the site of the tumor. The magnet pulls the drug-carrying particles out of the blood vessel so that they lodge in the tumor. Although the technique is still experimental, early research is promising. Physicians are hopeful that it will bolster the effects of chemotherapy while avoiding some of the drugs’ side effects, such as hair loss and nausea.
In recent years, scientists have gained a new understanding about genes—the basic biological units of heredity—and the role they play in disease. This knowledge has set the stage for medical science to alter patients’ genetic material to fight or prevent cancer. Although the science of gene therapy is still in the early, experimental stages, researchers are hoping that in the future the therapy can be used to:
Researchers in gene therapy search for new ways to treat cancer and other genetic diseases
One of the challenges of gene therapy is finding safe and effective ways to deliver genes or genetically altered cells to the site of the tumor. Interventional radiologists, with their special expertise in using X-rays and other imaging techniques to guide catheters and other tools through the body are expected to play an important role in this new technology.